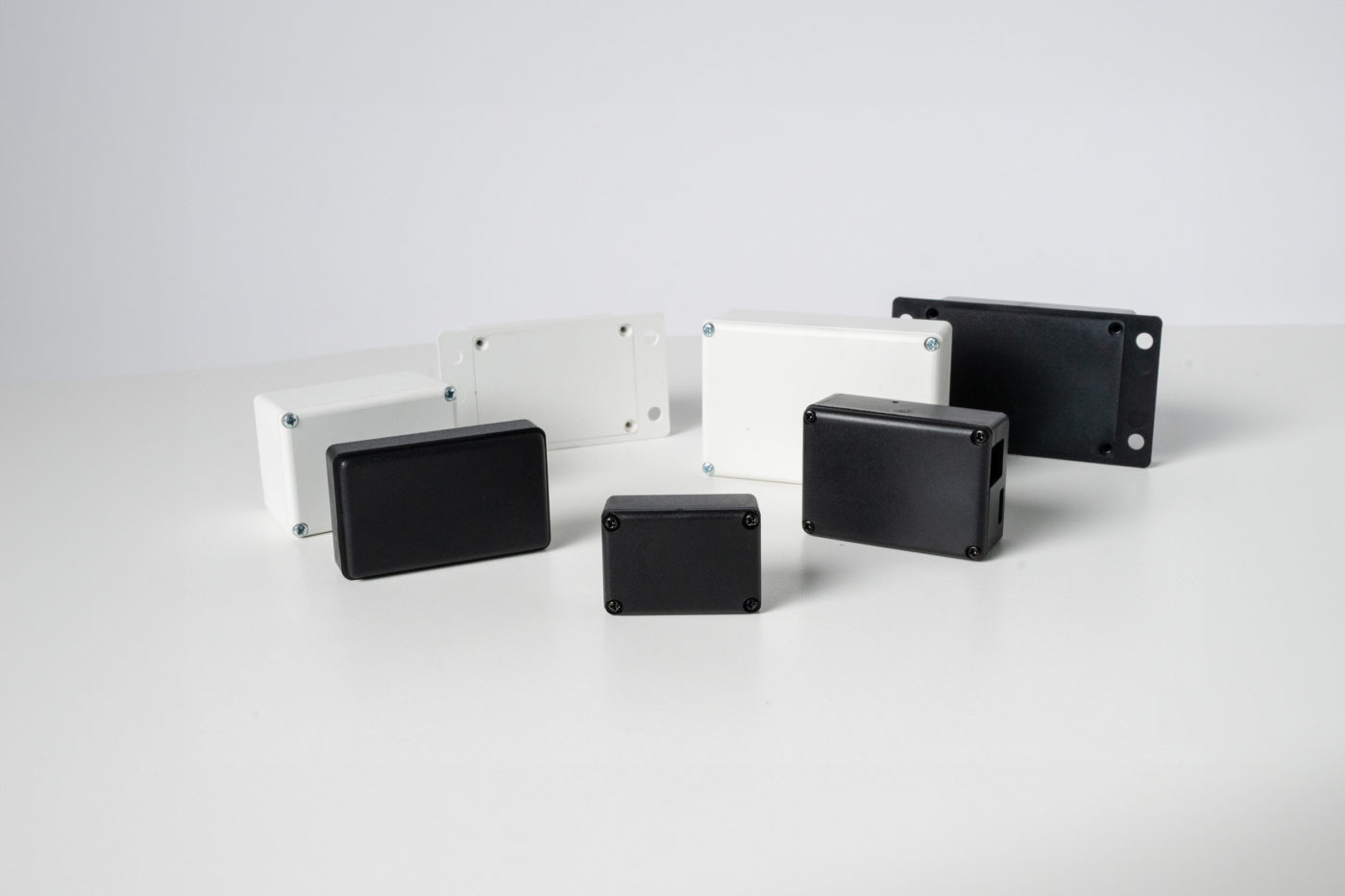





When designing electronic devices, protection is just as important as performance. One of the most effective ways engineers safeguard circuits is by using potting boxes – enclosures that are filled with resin or gel to completely encapsulate sensitive components.
In this guide, we’ll look at what potting boxes are, why they’re used, the materials involved, and the design considerations you should keep in mind.
A potting box is designed to house a PCB or component in protective material. This process, known as potting, transforms a fragile circuit into a rugged, sealed, and tamper-resistant module. The main benefits include:
The enclosure itself is usually plastic, which is then filled with a potting compound. The most common materials include:
Each compound has its advantages and trade-offs in terms of hardness, flexibility, and ease of servicing.
Before committing to potting a circuit, it’s important to take these factors into account:
Taking these into consideration during the design stage can help avoid costly problems later.
Potting boxes are used across a wide range of industries where reliability is non-negotiable, including:
Wherever electronics need to withstand demanding environments, potting boxes provide proven protection.
Potting boxes may look like a simple enclosure, but they play a vital role in extending the life and reliability of electronic devices. By selecting the right compound and designing with protection in mind, you can help ensure your circuits withstand moisture, vibration, heat, and tampering.
If you’re planning your next project, view our range of potting boxes to find the right solution for your application.